How Can You Compare Copper Vs. Aluminum Heat sink?
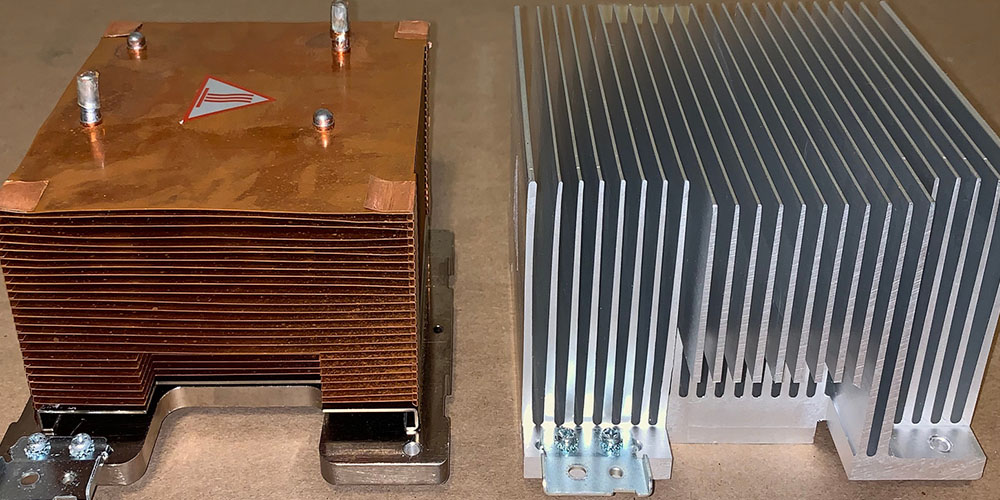
Heat sinks are essential for transferring heat away from cooling-required equipment electronic parts and other applications. Copper and aluminum are two of the most often used materials when it comes to heat sinks. These metals have distinctive qualities that make them suitable for various purposes.
Heat sinks function by transferring heat away from machinery, electrical components, or other applications. The heat from the hot component is absorbed by the heat sink which then disperses it over a greater surface area for more effective heat dissipation.
Materials designed for the efficient control of the heat temperature of any mechanical or electronic device are called heat sinks. Aluminum and copper alloys are the two materials that are utilized for heat sinks the most frequently. We will contrast copper vs aluminum heatsink in this article and examine which is better for you.
What Do You Know about Copper & Aluminum Heat sink?
Copper alloys or pure copper are used to making copper heat sinks. Copper is a highly conductive metal that effectively conducts heat away from machinery such as motors and electrical components. Because of its superior thermal conductivity high melting point and high ductility, copper heat sinks are utilized extensively in a wide range of applications.
Aluminum alloys or pure aluminum are used to make aluminum heat sinks. Aluminum is a thin highly conductive metal that is also lightweight. Due to their superior thermal conductivity lightweight low cost and resistance to corrosion aluminum heat sinks are frequently utilized in a variety of applications.
Applications of the Copper and Aluminum Heat sink
Heat sinks made of copper and aluminum are frequently utilized in a variety of applications, such as:
Inverter Cooling
Electronic equipment known as inverters change DC electricity into AC power. Heat sinks made of copper and aluminum are frequently utilized to reduce inverter heat.
Coolant for IT Telecommunications
Servers, routers, and switches, as well as other IT and telecommunications equipment, are cooled using copper and aluminum heat sinks.
Coolant for Motor Housing
When a motor is operating, heat is produced, and this heat must be removed to keep the motor in good condition. Heat sinks made of copper and aluminum are frequently used in motor housing to keep the motor cool.
Units for Welding
To keep the welding equipment from being harmed, heat generated during welding needs to be extinguished. To reduce the heat produced during welding, copper and aluminum heat sinks are frequently utilized in welding equipment.
Choosing the Right One Heatsink
The unique application requirements determine whether to use copper or aluminum heat sinks. For applications that demand quick heat transmission and strong thermal conductivity, copper heat sinks are a superior choice.
Applications that call for cost-effective, lightweight, and moderate heat transfer are better suited for aluminum heat sinks. It is crucial to take into account aspects like heat dynamics, thermal conductivity, cooling, weight, costs, and availability when deciding between copper and aluminum heat sinks.
Last Wording
Both copper and aluminum heat sinks are great options for transferring heat away from machinery, electronic components, and other cooling-required applications. Aluminum is a lightweight, cost-effective material that is better suitable for applications that require moderate heat transmission and are on a tight budget, whereas copper has a higher thermal conductivity and is better suited for applications that demand quick heat transfer.


